
Mikoa maskini Tanzania 2023, kiwango cha umaskini Tanzania. Dr. Philip Mpango, the Vice President of Tanzania has said “The main goals of the 2025 vision, a better life for every Tanzanian, maintaining peace, security and unity in the country, good governance, a well-educated and learning society, five are a strong and competitive economy.”
Despite the big steps that the country has taken, there are still various challenges that caused the goals of the National Development Vision 2000-2025 not to be fully achieved, for example:
Mikoa maskini Tanzania 2023
According to the Income and Household Survey the regions have the Highest level of poverty. Some of the reasons mentioned to cause this situation are Historical Problems and Poor Infrastructure
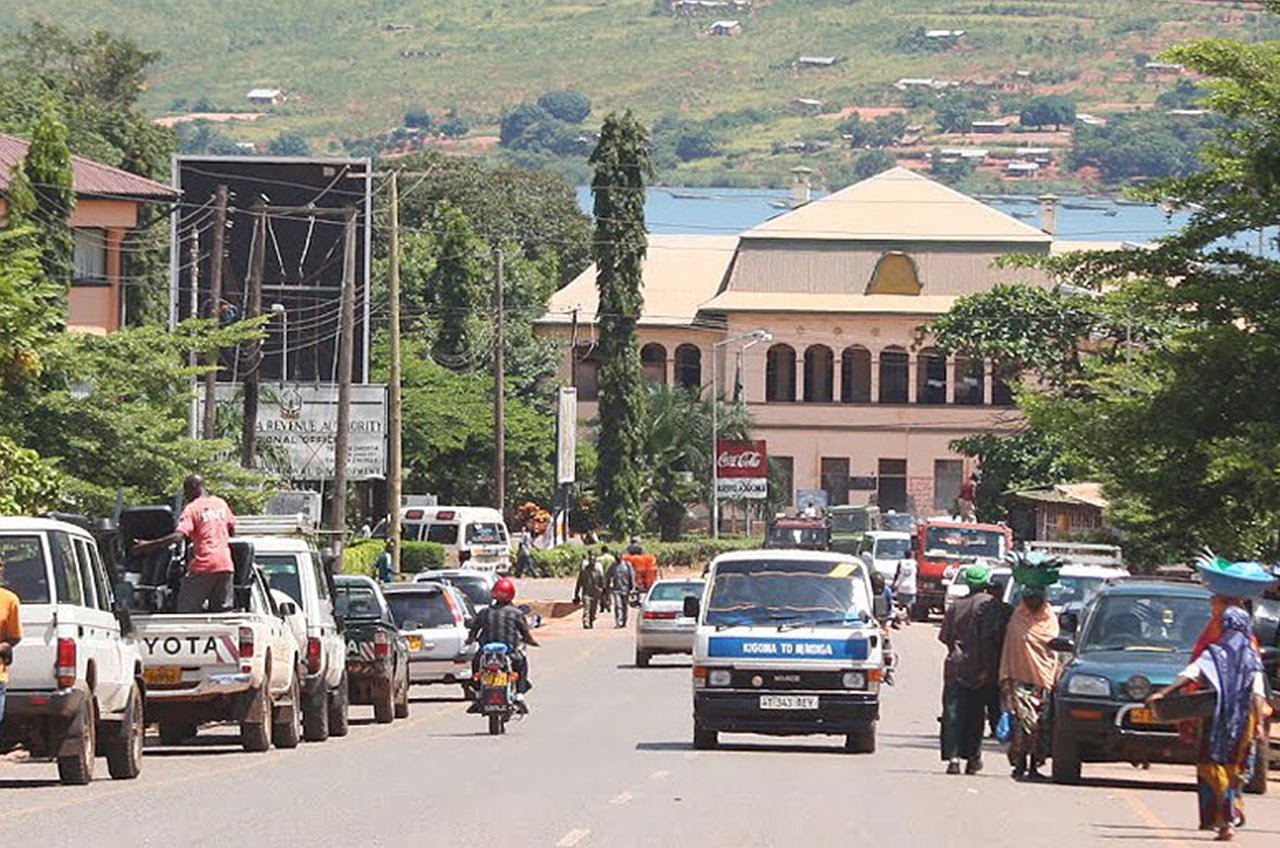
1. KAGERA
Kagera region is located in the North West of Tanzania. The Regional Headquarters is located in the city of Bukoba, 1500 kilometers from Dar es Salaam. This region borders Uganda to the North, Rwanda and Burundi to the West, Geita and Kigoma Regions, to the South.

The local economy of Kagera region was based on banana and coffee plantations. Their staple food is bananas in their various forms. In their fields, they cultivate other crops according to the season. The crops include beans, cassava, corn and vegetables.
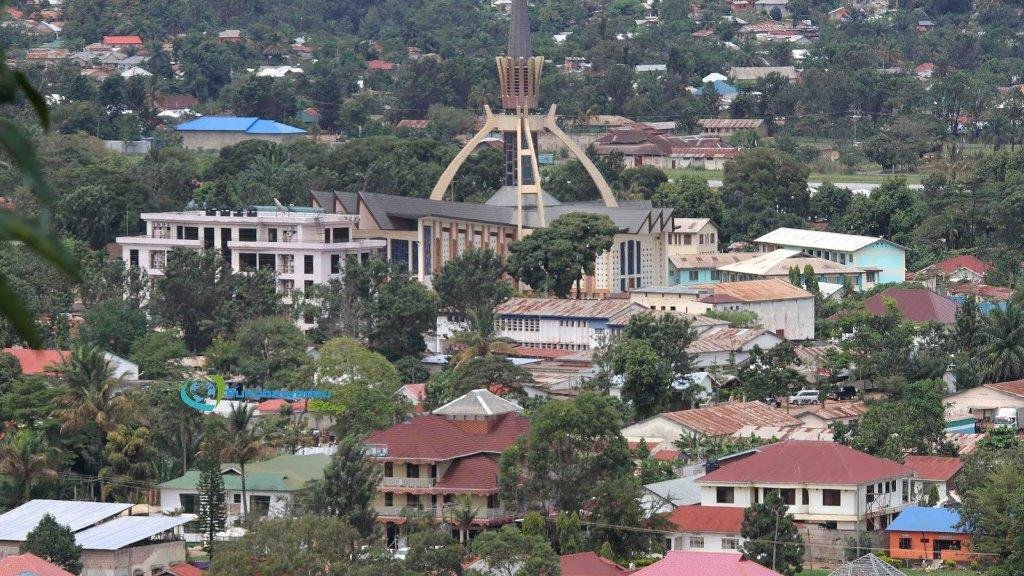
2. KIGOMA
Kigoma Region is one of the regions of Mainland Tanzania with enough fertile land, natural vegetation and an attractive climate. The region also has rare biodiversity that attracts tourists from within and outside the country.

There are mountains, valleys, rivers and Lake Tanganyika, which is the second deepest in the world. In general, the geography of Kigoma Region makes it a strategic Region for tourism investment, agriculture, industry and business. In addition, economic activities in the Region have continued to improve due to the Government’s efforts to improve various social services, road infrastructure, railways, electricity and air transport.
3. SINGIDA
Singida region is located in the middle of mainland Tanzania. Its capital is Singida and it is an important crossroads for road transport to the North, West, South and East. Singida is bordered by Manyara Region to the North, Dodoma Region to the East, Mbeya and Iringa Regions to the South and Tabora and Simiyu Regions to the West.

Regional income is Shs. 978,701,000 while the per capita income is Shs. 697, 667 according to the information of 2013.
Economic activities in Singida Region include agriculture which employs an average of 86 percent of all residents. Priority crops in terms of food are sorghum, millet, cassava and sweet potatoes and in terms of commercial crops are sunflowers, onions, cotton and sesame.
4. TABORA
Tabora region is among the 31 regions of Tanzania with postcode number 45000. Its headquarters are in Tabora City. Tabora is the name of a town, district and region in central Tanzania. The area of the region is 76,151 km2; in km2 34,698 (46%) are forest reserves, 17,122 km2 (22%) are animal reserves.
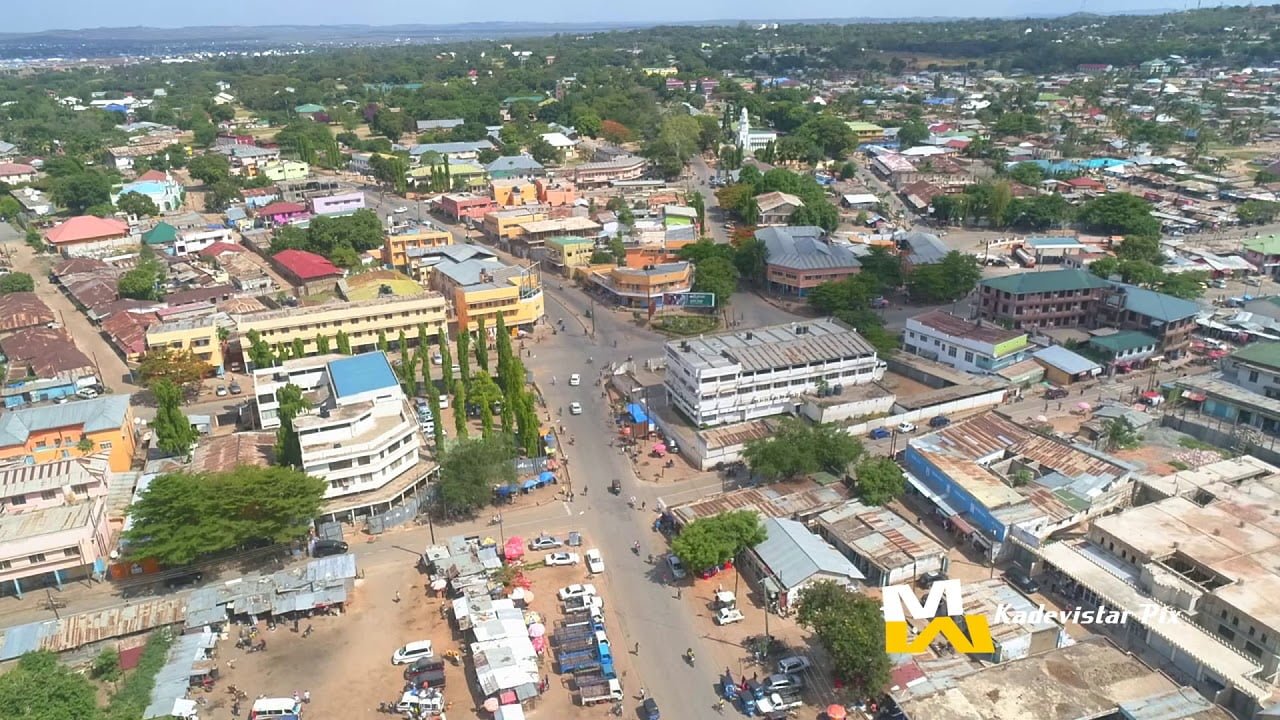

The total population was 3,391,679 people (2022). The natives of Tabora are mainly Wanyamwezi. Most of them are farmers and breeders.
5. DODOMA
Dodoma Region lies inland very close to the centre of Tanzania Mainland. Its location attracts the Tanzania Government to establish its Capital in Dodoma Municipality. Dodoma Region is located south of the equator between latitudes 6° 57′ and 3° 82′. Longitudinally the Region is situated between 36° 26′ and 35° 26′ east of Greenwich.
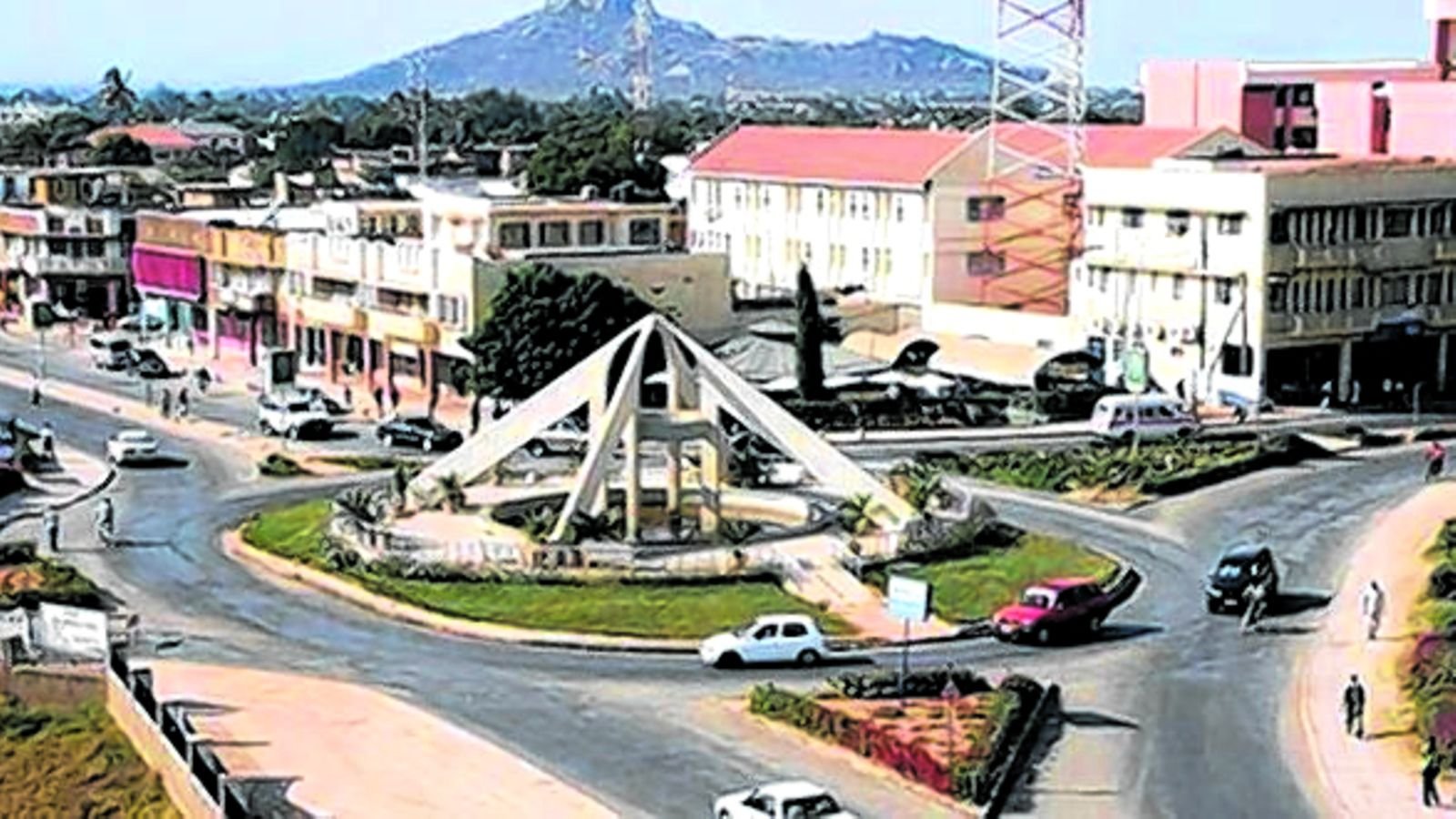

It boarders four Regions namely Manyara, Iringa, Singida and Morogoro. It is accessible from Manyara through Babati and Kateshi in Manyara Region; Dar es Salaam and Pwani through Morogoro and Tabora, Shinyanga and Mwanza through Manyoni in Singida Region. All the Roads are accessible through out the year.
Poverty in Tanzania
“The challenge of income poverty and poor nutrition, according to the study of Income and Household, approximately 26.4% of Tanzanians live below the income poverty level, which is more than a quarter and the poorest citizens live in rural areas 31.3%.
There are regions, I will mention a few Kagera, Kigoma, Singida, Tabora and Dodoma where the level of poverty is higher due to various reasons including historical problems and poor infrastructure.
In addition, the income gap among Tanzanians has continued to increase despite doing well in the criteria of doing well in the overall economy.
The level of income difference using the proportional measure increased from 0.34 in 2011/12 to 0.38 in 2017/18.
In the same period, the measure of income disparity for Urban areas also increased from 0.37 to 0.41.
30% of children under the age of five are stunted in the country
Speaking at the launch of the Preparation Process for the National Development Vision 2050, the Vice President, Dr. Philip Mpango has said that these figures are according to the study of Income and Household.
He said “Maternity and Child Health Research and Malaria indicators for the year 2022 show that 30% of Children under five years of age have stunting and 9% of Children have severe stunting.”
Dr. Plan: Our education does not meet the needs of the labor market
In terms of having an educated and learning society, we have achieved satisfactory results including an increase in students at all levels of education.
Success rates have increased, literacy in the country is estimated at 92%.
Despite these successes, many young people who complete their studies do not find employment opportunities, also our education does not meet the needs of the labor market or enable graduates to be self-employed.
Efforts to correct the situation are ongoing, including through education policy and curricula.












Kama ndohivo jameni tuangaliwe watoto wa maskini